Deferrals, on the other hand, are when an organization has received a pre-payment for a service or product that is not yet earned or they have paid for an expense which is yet to be incurred. Accrual records payments and receipts when services or good are provided or debt is incurred. Accrual accounting uses the double-entry accounting method, where payments or reciepts are recorded in two accounts at the time the transaction is initiated, not when they are made. The general concept of accrual accounting is that accounting journal entries are made when a good or service is provided rather than when payment is made or received. The matching principle is a cornerstone of accrual accounting, requiring that expenses be recorded in the same period as the revenue they support. Some expenses relate to obligations that extend over many yeats, such as warranties, service agreements, or lease payments.
Get in Touch With a Financial Advisor
- Similarly, a company may have incurred interest expense on a loan, but the payment has not yet been made.
- The key advantage of the cash method is its simplicity—it only accounts for cash paid or received.
- For instance, a company might pay an annual premium in January for coverage extending through December.
- While accrual accounting provides a more accurate financial picture of a company’s operations, it is not without its challenges.
- Fyle’s AI checks if expenses align with preset business rules before submission, flagging potential fraud or duplicate entries automatically.
Even for smaller businesses, using the expense recognition principle can provide better clarity and support growth through accurate reporting. Advertising costs are often discretionary, so applying the expense recognition principle helps business evaluate the ROI of their marketing strategies more accurately. Training should include updates on relevant accounting standards, software training, and case studies to illustrate complex scenarios.

Cash Basis Accounting
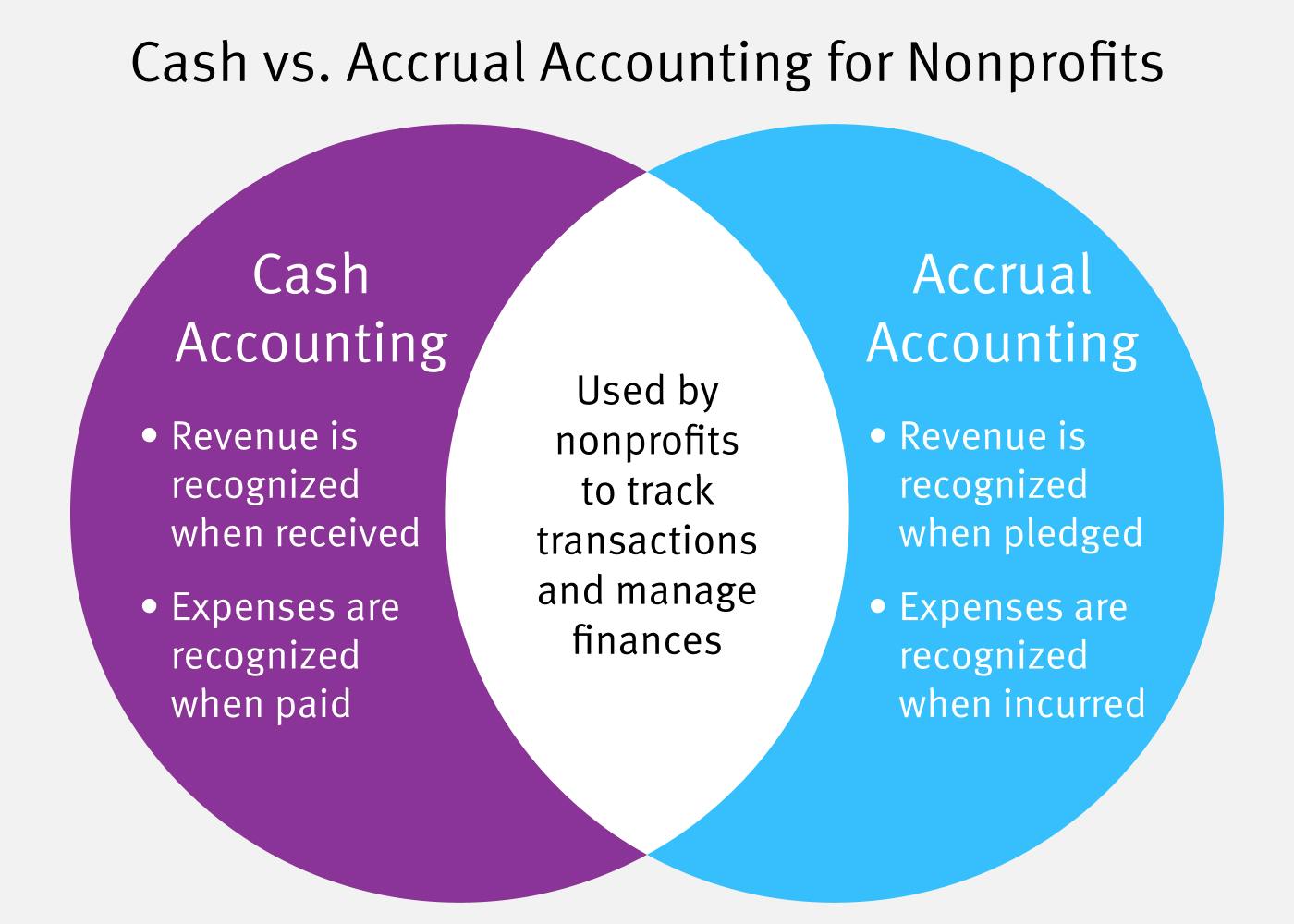
While cash basis accounting records transactions when cash is received or paid, accrual accounting records transactions when they occur, regardless of when cash is received or paid. Let’s assume that I begin an accounting business in December and during December I provided $10,000 of accounting services. Since I allow clients to pay in 30 days, none of the $10,000 of fees that I earned in December were received in December. Under the accrual basis of accounting my business will report the $10,000 of revenues I earned on the December income statement and will report accounts receivable of $10,000 on the December 31 balance sheet.
Example of Reporting Revenues Under the Accrual Basis of Accounting
This matters because if you only tracked cash, it would look like you didn’t make any money in December. But by recording the revenue in December, you get a more accurate picture of your company’s performance for that period. It also helps you plan your budget and see if you met your goals for the year, even if the payment comes later.
Firm of the Future
When using accrual accounting, you’ll have different adjusting entries to add to the balance sheet and income statement. Has your business reached the point where you’re ready to hire more employees or expand into new customer markets? As your business becomes more complex, it may be time to revisit whether accrual accounting will be more effective for your financial and tax reporting.
This approach diverges from traditional methods by recognizing the economic impact of transactions at the time they happen, not just when cash is exchanged. A company with a bond will accrue interest expense on its monthly financial statements even though interest on bonds is typically paid semi-annually. The interest expense recorded in an adjusting journal entry will be the amount that’s accrued as of the financial statement date. It will also be reflected in the receivables account as of December 31 because the utility company has fulfilled its obligations to its customers in earning the revenue at that point. The adjusting journal entry for December would include a debit to accounts receivable and a credit to a revenue account. The company would record a credit to decrease accounts receivable and a debit to increase cash the following month when the cash is received.
The 2023 financial statements must reflect the bonus expenses earned by employees in 2023 as well as the bonus liability the company plans to pay out. An adjusting journal entry therefore records this accrual with a debit to an expense account and a credit to a liability account before issuing the 2023 financial statements. A cash basis system is much simpler (and less costly) than the accrual accounting method, but it won’t work for every system.
Accrual accounting is crucial for SMEs as they engage in credit transactions, helping them accurately track owed revenue and expenses. This then offers a realistic view of cash flows and financial obligations, which is essential for SMEs in making informed decisions about their operations and investments. evolution of business and why every organization needs to embrace caring leadership In the matching principle, an organization recognizes the expenses incurred and revenues generated both in the same financial period. Accrual accounting allows you to get a better, more accurate view of your organization’s finances at present and in the long run by combining cash inflows/outflows.
When a company pays cash for a good before it is received, or for a service before it has been provided, it creates an account called prepaid expense. This account is an asset account because it shows that the company is entitled to receive a good or a service in the future. Accrual accounting is helpful because it shows underlying business transactions, not just those with cash involved. Most transactions a company has are straightforward, with payment happening at the time of the transaction.
This ensures that the insurance cost reflects its actual benefit across the coverage period, aligning expenses with the relevant accounting periods. For example, if a business runs an advertising campaign in December but expects increased sales in January and February, the cost could be allocated over those months. For companies dealing with international expenses, foregin currency fluctuations can complicate expense recognition. Changes in exchange rates between the time an obligation is incurred and when it is paid can lead to variances in expense recognition. This method is particularly useful for ensuring accuracy when dealing with long-term expenses, such as depreciation or prepaid expenses.
The key advantage of the cash method is its simplicity—it only accounts for cash paid or received. The intricacies of accrual accounting reveal its pivotal role in modern business and finance. While complex, this approach opens up a world of accuracy and insight into the financial workings of a company.
